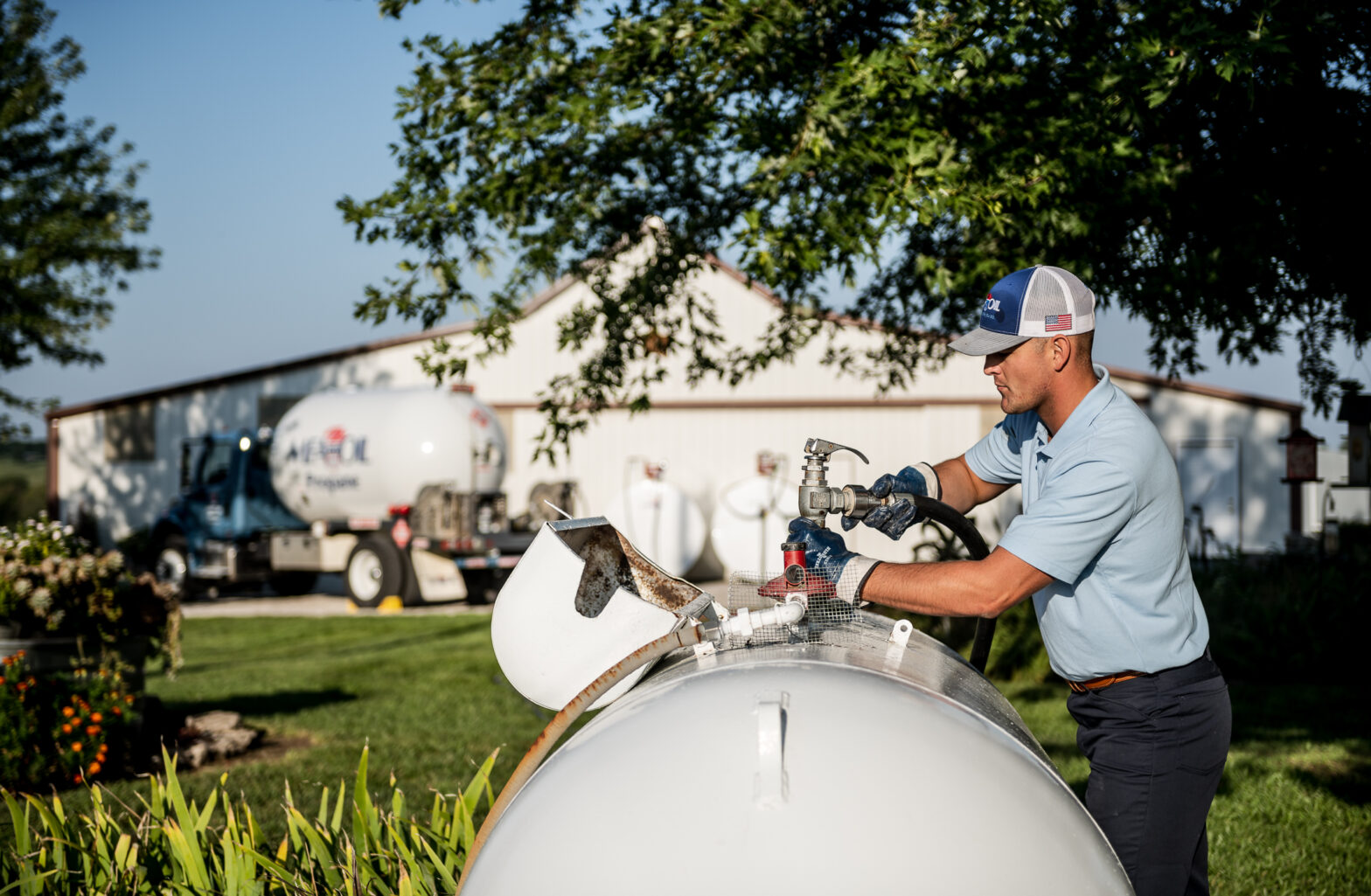
Maximizing Efficiency: Why Propane is the Smart Energy Choice
Whether you run a restaurant, manage a fleet, or operate a large commercial facility, propane provides the versatility and dependability your business needs to succeed. Here’s how propane can make a difference in your operations and why it’s a wise choice for business owners of all kinds. Cost-Efficient Heating and Hot Water Solutions Keeping operating… Continue reading Maximizing Efficiency: Why Propane is the Smart Energy Choice